Bone Marrow Aspirations and Biopsy, Lymph node FNAC
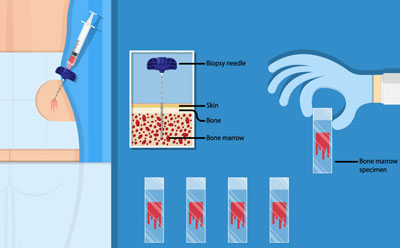
Bone Marrow Aspirations and Biopsy and Lymph Node Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) are diagnostic procedures used to investigate a variety of hematological and oncological conditions. These procedures help in diagnosing blood disorders, cancers, and infections.
Bone Marrow Aspirations and Biopsy
- Bone Marrow Aspiration:
Purpose: A bone marrow aspiration involves taking a small sample of bone marrow (the soft, spongy tissue inside the bones) for examination. It is commonly done to evaluate blood disorders such as anemia, leukemia, or myelodysplastic syndromes. - Bone Marrow Biopsy:
Purpose: Bone marrow biopsy involves removing a small cylinder (core) of bone marrow tissue, often to assess marrow architecture, cell types, and any disease involvement. It is used when more detailed analysis is required.
Indications for Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy:
- Unexplained anemia, thrombocytopenia, or leukopenia.
- Diagnosis of leukemia, lymphoma, or other hematological cancers.
- Investigating myelodysplastic syndromes, bone marrow failure, or aplastic anemia.
- Assessing the spread of cancer or metastasis to the bone marrow.
Lymph Node FNAC (Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology)
Purpose of Lymph Node FNAC:
- Lymph Node FNAC is a procedure used to extract a small sample of tissue from a swollen lymph node to diagnose conditions like lymphoma, tuberculosis, metastatic cancer, or infections.
- It involves inserting a fine, hollow needle into the lymph node and extracting a sample of cells, which are then examined under a microscope.
Indications for Lymph Node FNAC:
- Investigation of unexplained, enlarged lymph nodes.
- To diagnose lymphoma, metastatic cancers, tuberculosis, and various infections.
- Monitoring known cancers for recurrence or spread.
Advantages of FNAC:
- Quick and minimally invasive.
- Typically requires no hospitalization.
- Low risk of complications like bleeding or infection.
