Bone Marrow Transplantation (Autologous and Allogeneic HSCT)
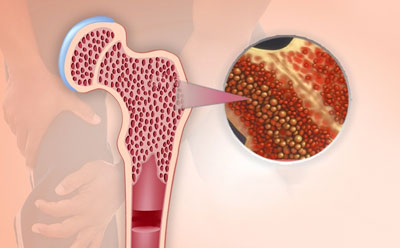
Bone marrow transplantation (BMT), also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), is a specialized medical procedure used to treat a variety of hematological disorders, cancers, and immune deficiencies. The procedure involves replacing damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells capable of regenerating functional blood cells.
Types of Bone Marrow Transplantation
Autologous Transplantation:
- In this method, a patient's own stem cells are collected, processed, and stored before undergoing high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- The stored stem cells are reinfused into the patient to restore bone marrow function.
- Commonly used for diseases like multiple myeloma and certain lymphomas.
Allogeneic Transplantation:
- Stem cells are obtained from a donor whose tissue type matches the patient (HLA-matched donor).
- The donor may be a family member, an unrelated donor, or, in some cases, umbilical cord blood.
- This approach is often used for leukemia, severe aplastic anemia, and other genetic or immune disorders.
Indications for Bone Marrow Transplantation
Hematological Malignancies:
- Leukemia (Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia).
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS).
- Lymphomas.
Non-Malignant Disorders:
- Aplastic anemia.
- Sickle cell disease and thalassemia.
- Immune deficiencies and autoimmune diseases.
Advantages of Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Provides a potential cure for many life-threatening conditions.
- Replaces defective bone marrow with healthy cells, restoring normal blood cell production.
- Allogeneic BMT offers the possibility of a graft-versus-tumor effect, where donor cells attack residual cancer cells.
